NAND2Tetris
Part 1
Table of contents
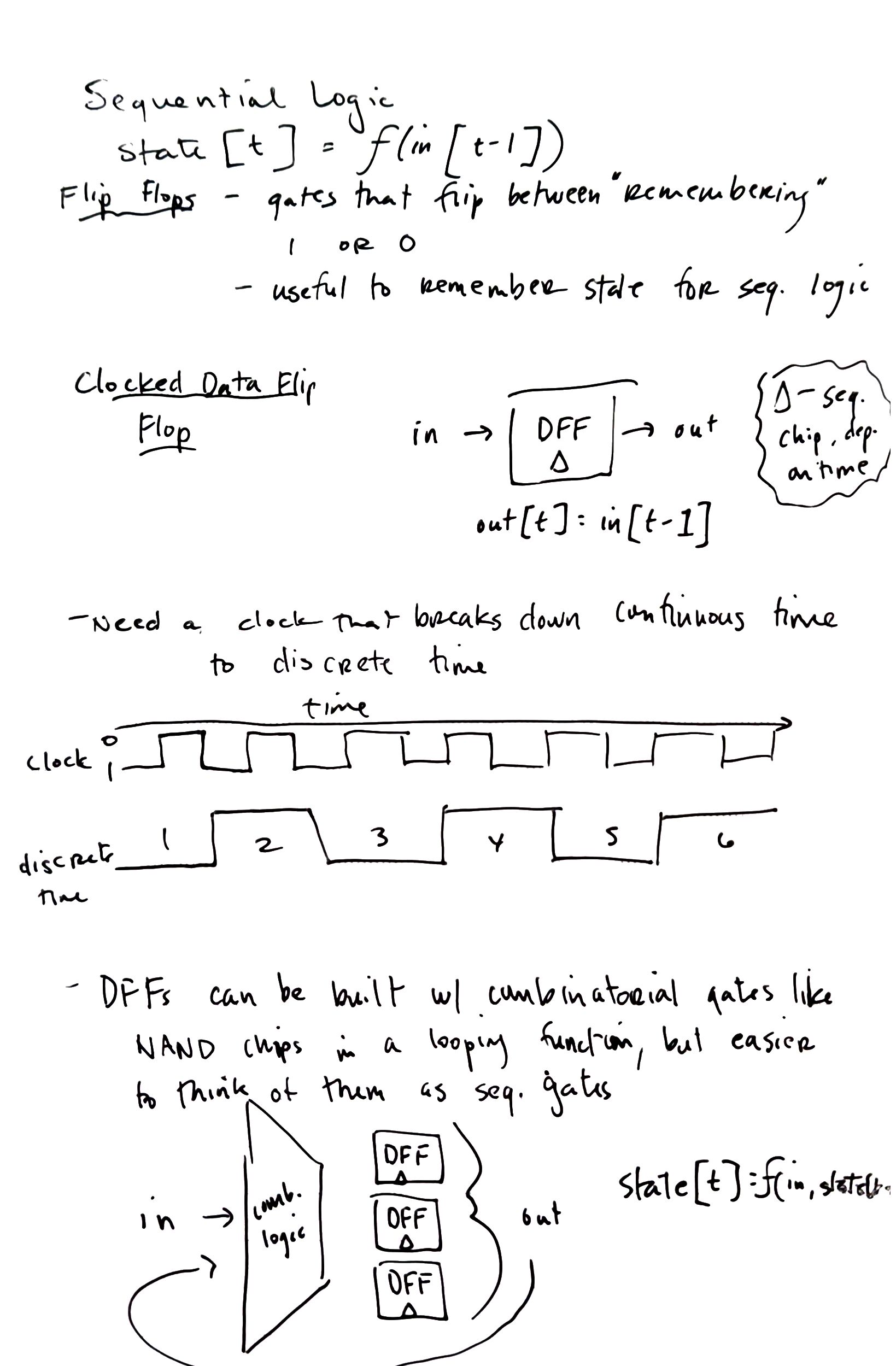
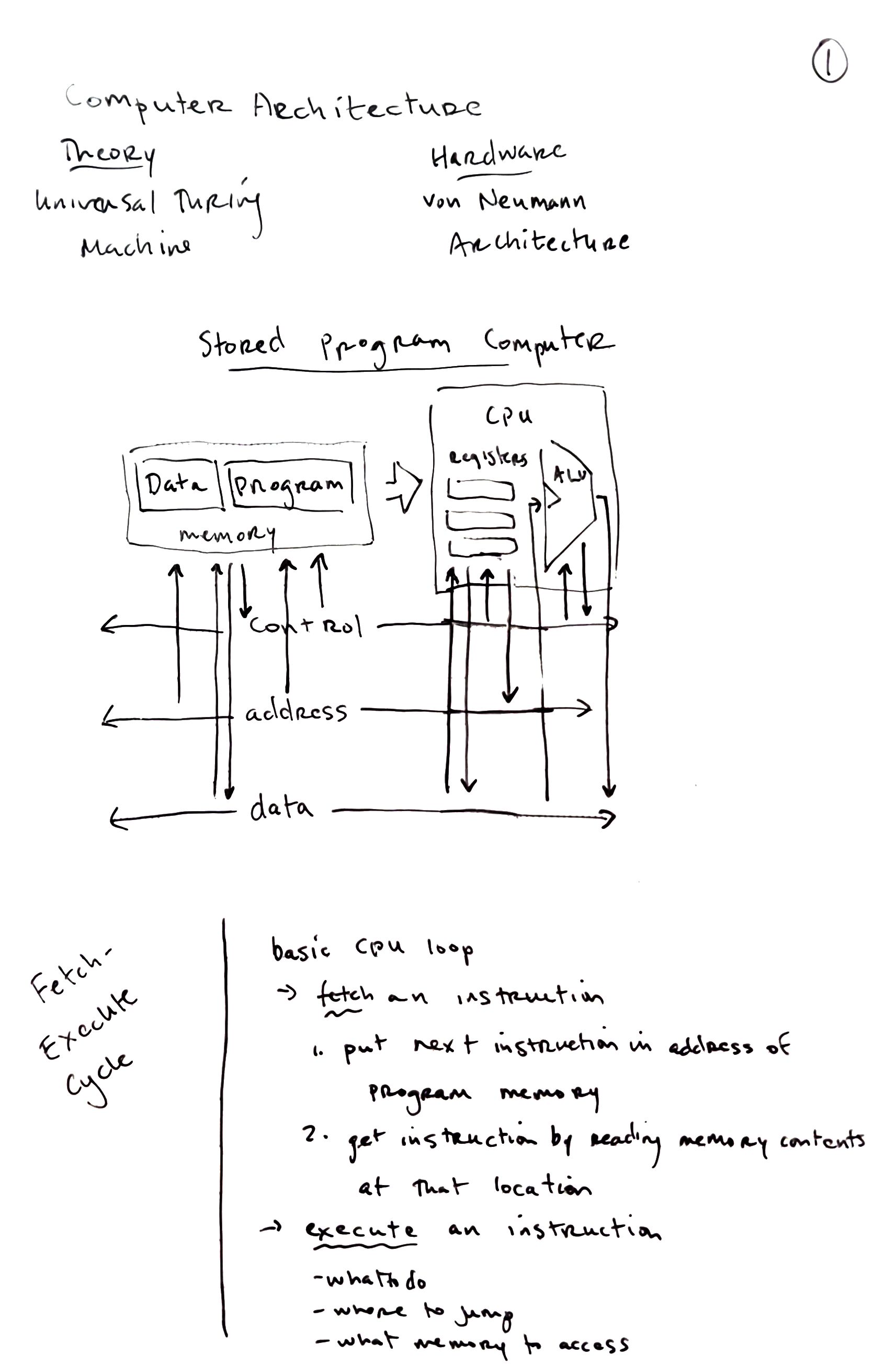
Boolean Logic
- truth table – gives all possible outputs of inputs, another way of representing boolean function
- unary operation – only takes single input
Boolean Identities
commutative laws
(x AND y) = (y AND x)
(x OR y) = (y OR x)
associative law
(x AND (y AND z)) = ((x AND y) AND z)
(x OR (y OR z)) = ((x OR y) OR z)
distributive law
(x AND (y OR z)) = (x AND y) OR (x AND z)
(x OR (y AND z)) = (x OR y) AND (x OR z)
de morgan laws
NOT(x AND y) = NOT(x) OR NOT(y)
NOT(x OR y) = NOT(x) AND NOT(y)
Boolean Function Synthesis
- any boolean function can be represented using an expression containing NAND operations
(x NAND y) = NOT(x AND y)
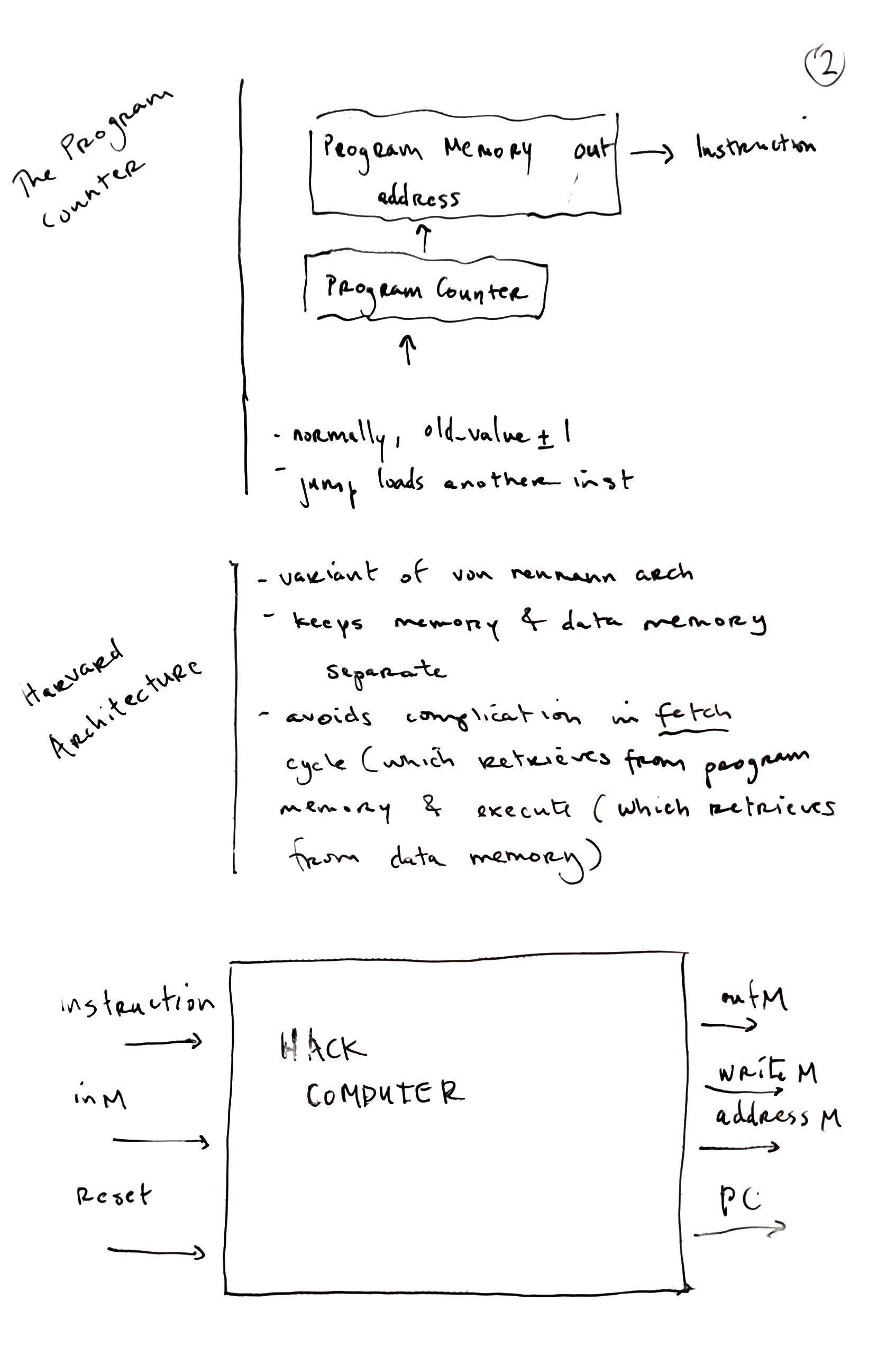
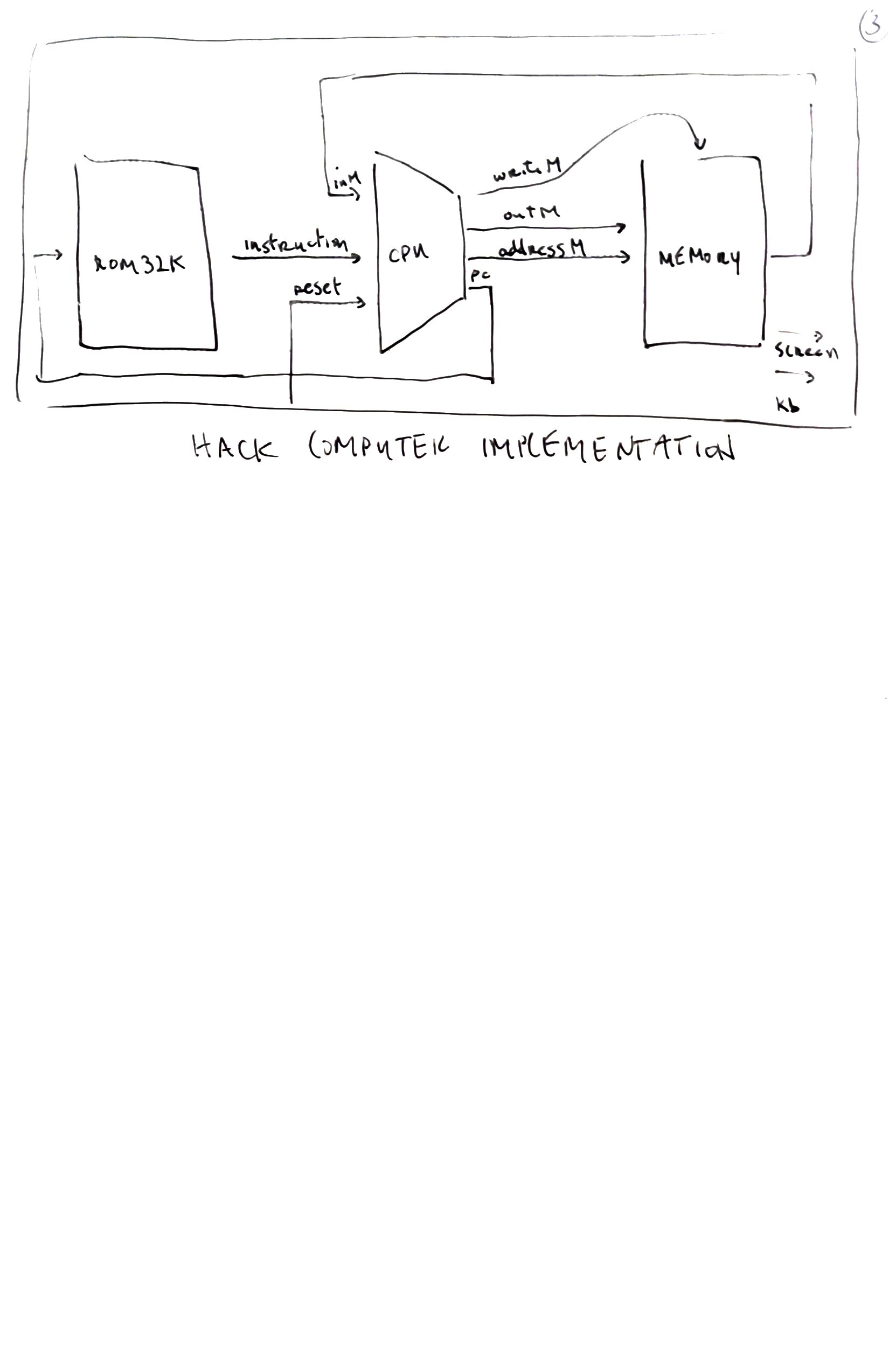
Logic Gates
- technique for implementing boolean functions using logic gates
- elementary (NAND, AND, OR, NOT, etc.)
- composite (MUX, ADDER, etc.)
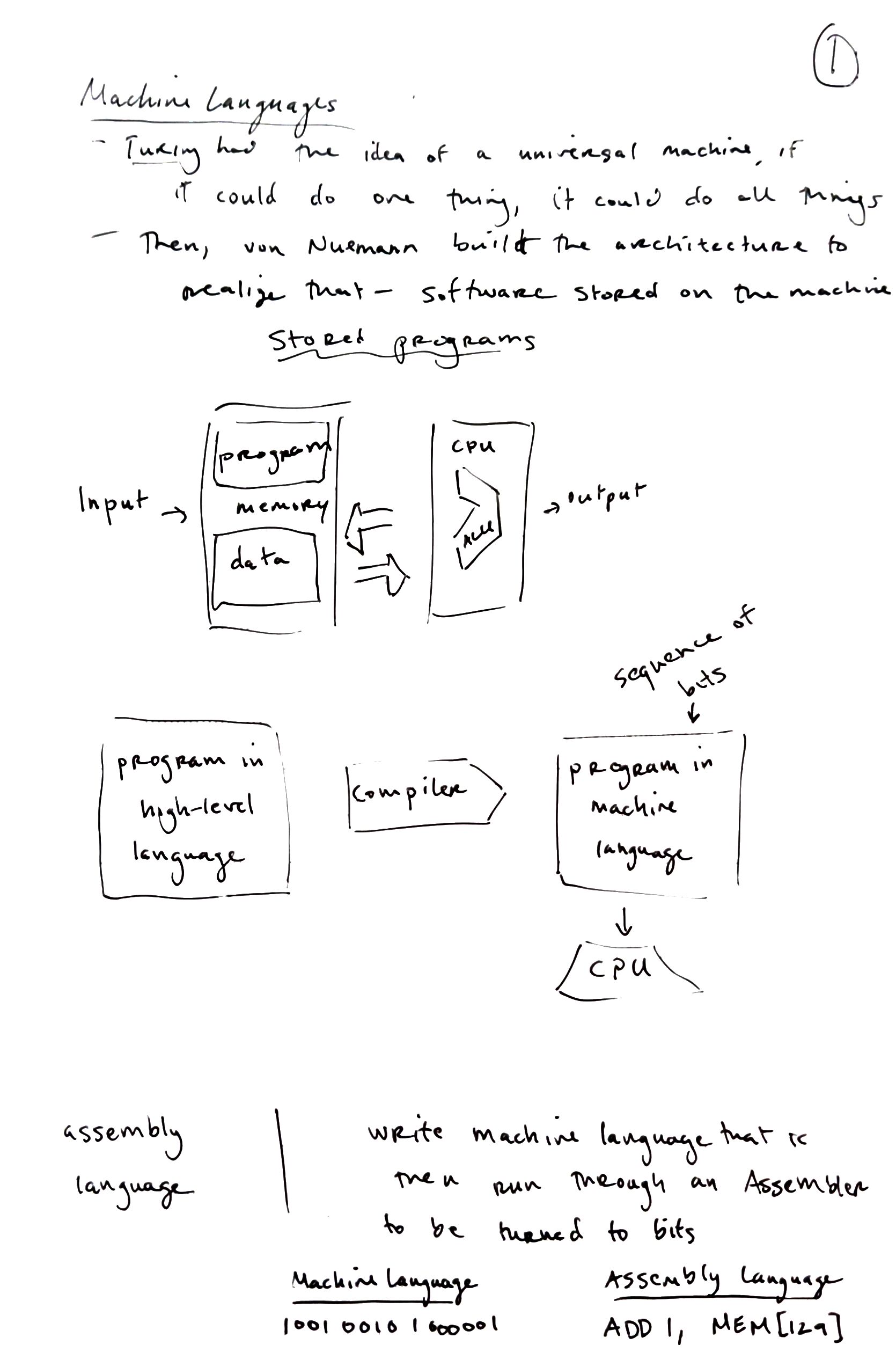
Hardware Description Language
Hardware Simulation
- interactive simulation – active tests
- script-based simulation – pass input and output into simulator
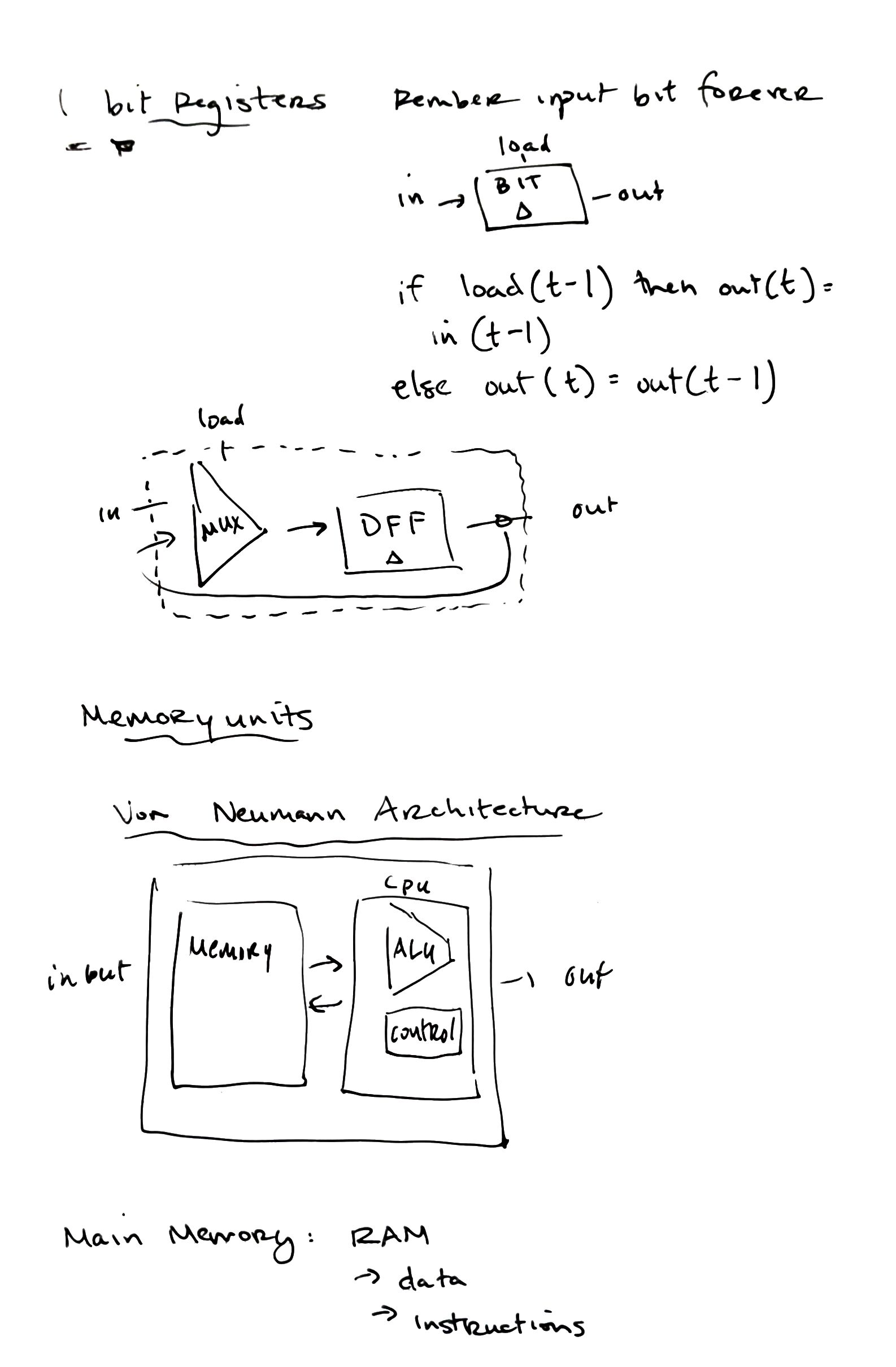
Boolean Arithmetic
convert binary to decimal
1
2
3
4
5
6
1101
2^4 2^3 2^2 2^1
8 4 2 1
1 1 0 1
8 + 4 + 0 + 1
13
convert decimal to binary
1
2
3
4
99
64 + 32 + 2 + 1
64 32 16 8 4 2 1
1 1 0 0 0 1 1
overflow – if adding numbers that carry over (carry bit), most computers ignore or truncate results
- only need to implement addition and subtraction, can handle multiplication and division in software where it is easier
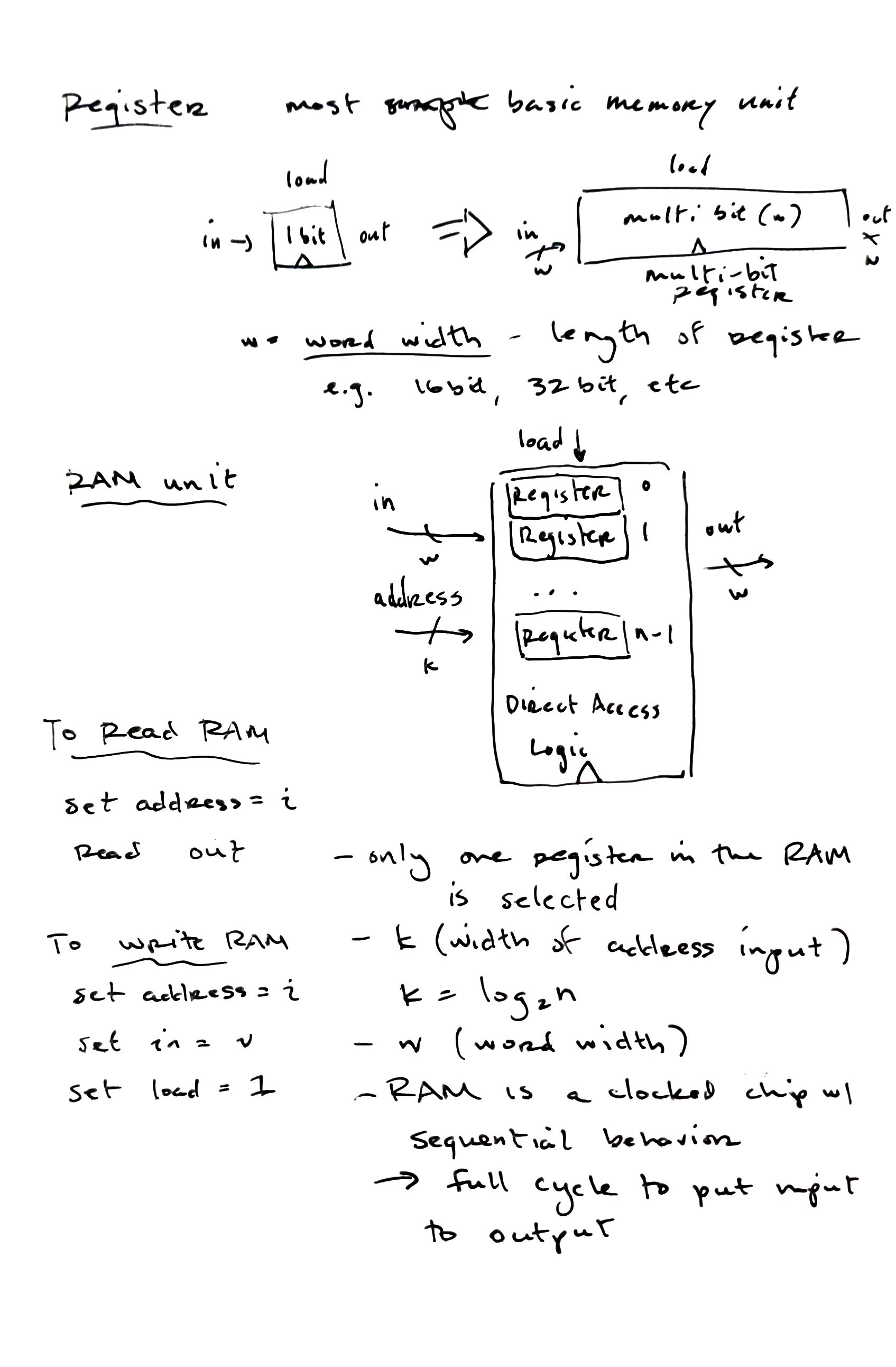
half adder chip
| a | b | sum | carry |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
full adder chip
| a | b | c | sum | carry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
convert to negative, flip bits and add 1